When the ground freezes, it becomes a hydraulic ram, crushing or twisting anything in its way. Water expands by 9% when it freezes, which can move footings, foundations, and pipelines underground.
The frost line is a critical area of concern for any external construction, from oil pipelines to backyard fences. To prevent frozen pipes and footings from shifting, contractors and DIYers need to understand what a frost line is and the frost level in your area. In this post, you’ll learn how to determine frost depths, how deep you need to dig to get below the frost line, and how to thaw frozen ground quickly if you must dig in winter.
Let’s start with the basic definition of the frost line.
What Is a Frost Line?
The frost line, also referred to as ground freezing depth, is the typical depth at which the ground freezes each year. Harsher winters result in a deeper frost line, requiring water pipes and cement footings to be buried further to prevent damage. The frost line extends from the top of the soil to a variable depth, depending on climate conditions, but thaws out during the warmer months.
It is important to note that frost lines differ from permafrost, a subsurface layer of permanently frozen ground found in northern regions like Canada and Alaska.
Why is Meeting the Frost Lines Important?
As water freezes, it expands. If you’ve ever left a can of soda in the freezer, you’ve seen how it swells and bursts—water and sewer pipes buried too shallow or buried above frost line depths face the same risk.
The International Plumbing Code states that “Exterior water supply system piping shall be installed not less than 6 inches (152 mm) below the frost line and not less than 12 inches (305 mm) below grade.”
Above the frost line, frozen ground can cause heaving, shifting structures, or even freezing the contents of pipes. To avoid these problems, knowing the frost level in your area ensures that pipes stay flowing, decks remain level, and foundations stay stable.
Want to save time and money when digging through frozen ground? The Powerblanket 5×9 Ground Thawing Heated Blanket can thaw 12-18 inches per day, allowing you to work efficiently even in frigid conditions. These blankets are durable, easy to use, and provide targeted heat exactly where you need it.
How Deep Does the Ground Freeze Go?
The frost line varies by location, with colder climates experiencing significantly deeper frost penetration.. Below is a general frost line map for the lower 48 states:
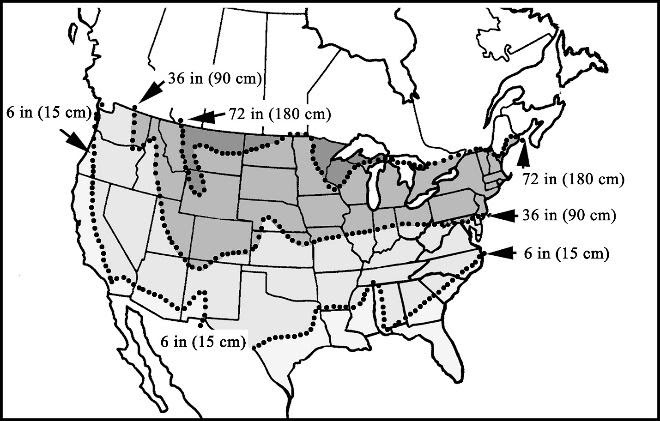
Frost Line Map
For the most accurate information on frost depth in your area, consult local building codes or a building inspector. They can provide a maximum frost depth map and specify the proper depth for footings and pipes.
You can see another interactive map that provides frost lines by state by hovering your mouse over the state.
Are There Any Formulas or Calculations That Can Estimate the Depth of the Frost Line?
Some equations can estimate or predict the frost line depth. Unfortunately, they are Ph. Ph.D.-level calculations, such as this Predictive Modeling of Freezing and Thawing of Frost-Susceptible Soils.
Some of the information and data that goes into calculating the depth of freeze or thaw include
- Maximum daily air temperature
- Minimum daily air temperature
- Estimated pavement surface temperature (for paved roadways)
- Frost depth
- Regression constant
- Average measured frost depth
The best way to find the frost level for your area is to call your local building code agency. They will have the most accurate information.
How Does the Frost Level Affect Digging in the Winter?
Frozen ground can be as solid as concrete. Manually, a pickaxe is the best option to break through the top layer, but it will be very slow going and not practical for long trenches. There are various powered options for Bobcats, backhoes, and excavators. Still, frozen ground is tough on machines and their operators.
For example, cutting through frozen soil with a trenching machine requires carbide teeth, which can cost $5 each. Some contractors report replacing up to 90 teeth per day, resulting in $450 in costs—or even $1,500 for a full chain replacement, plus labor and downtime.
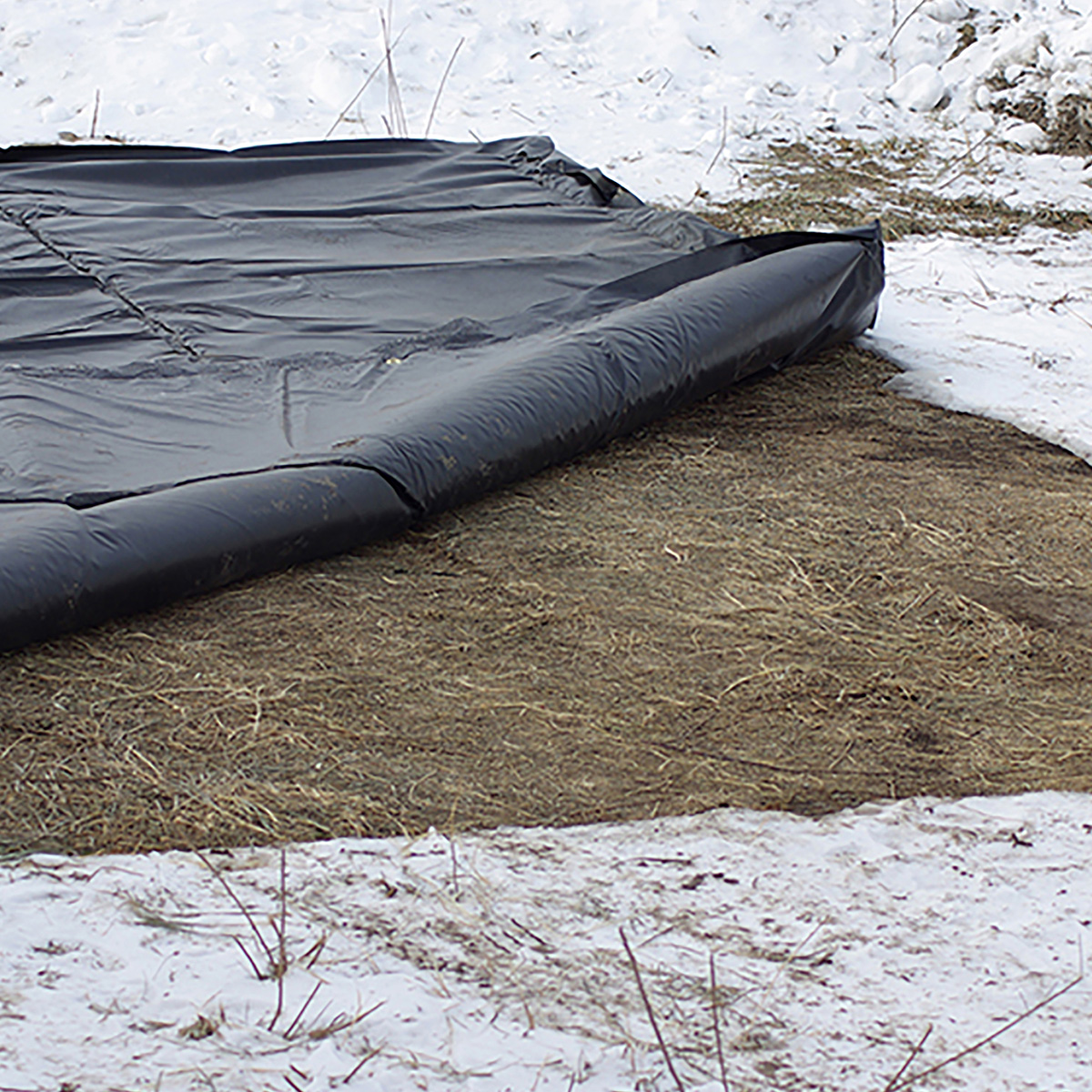
To avoid these costly delays, the best option is to thaw the ground first using ground-thawing blankets.
Ground Thawing Blankets Can Penetrate Frost Line Depths
Cold weather can have severe negative impacts on construction jobs, trenching, cemetery operations, and other outdoor projects. The best solution to quickly thawing frozen ground is Powerblanket ground thawing blankets.
A ground thawing blanket has heating elements that heat up to 150°F (65.5°C) and uses a standard electrical plug. Depending on soil conditions and ambient temperature, the heat can penetrate 12 to 18 inches deep within 24 hours.
It’s important to note that insulated concrete blankets are different from ground-thawing blankets. While insulated blankets only trap existing heat, ground-thawing blankets actively generate warmth, making them far more effective in frozen conditions.
Powerblanket Saves Time and Money
Construction projects can’t afford to wait for the ground to thaw. Busting through the ice-hardened ground is tough on man and machine. Powerblanket ground thawing blankets save many hours of labor. For example, one Idaho cemetery had a ground-freezing depth of 14 inches. Using the Powerblanket to thaw the ground saved hours of digging time. Additionally, they could roll up the sod and reuse it, saving $100 per grave.
Powerblanket ground thawing blankets come in various sizes, which you can compare here.
Frequently Asked Questions
How deep do you need to dig to get below the frost line?
The depth required to dig below the frost line varies by location, with colder climates needing deeper excavations, sometimes over eight feet, while warmer areas may require less than one foot.
What is the frost line and why is it important?
The frost line is the average depth the ground freezes annually, and it's crucial for construction to ensure water pipes and cement footings are buried deep enough to prevent damage from freezing and thawing cycles.
How do I find the frost line in my area?
To find the frost line in your area, contact your local building department or perform an online search using your city name and the term "frost depth."
How deep to bury water lines to keep from freezing?
Water and sewer lines should be buried at least six inches below the local frost line to prevent freezing, as recommended by building codes.
Time is money. Don't waste time waiting for the ground to thaw. Powerblanket has you covered.





